Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties
of the material are characterized by:
E-modulus, force-unit/area-unit
Poissons ratio, strain/strain
Thermal expansion, strain/temperature-unit
Eigen strain,
Creep-model
consisting of 2 serial connected Kelvin-elements
Stress in springs based
on total creep strain, Creep Model I:
![]()
The rate of creep-strain, ![]() , is
calculated from:
, is
calculated from:
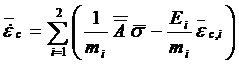
Stress in springs based
on incremental creep strain, Creep Model II:
![]()
The change of rate of
creep-strain, ![]() , is
calculated from:
, is
calculated from:
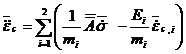
with
![]()
![]() is the accumulated stress
in the spring no. i.
is the accumulated stress
in the spring no. i.
![]()
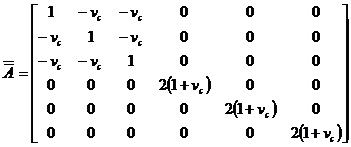
mi is the viscocity in Kelvin-element
no. i (force*time/area)
Ei is the springfactor in Kelvin-element no. i
(force/area)
εc,i is the total creep-strain in Kelvin-element no. i
![]() is the creeping Poissons ratio, see below.
is the creeping Poissons ratio, see below.
Creeping Poissons ratio,
The effect of the creeping
Poisson's ratio appears from the above shown matrix A.
General
All properties are
functions of maturity and are described by means of the function:
![]()
M is the
maturity
Qinit = Initial value
Qfinal = Final value
τe = Time Parameter, determining the maturity
where the sign of the curvature is changing
α = Curvature Parameter, describing how steep the rise
of the curve is
or
by means of a piecewise linear
curve.